November 27, 2018
The Excel COUNTIF Function is used to count the numbers in a given range, with an added logical condition to determine whether to add the number in the count.
Note
The criteria will typically be wrapped in double quotes, (”), for example, to count the items greater than 5 you would use the following criteria
">5"This is also true for logical test using dates
">1/07/2016"Usage
=COUNTIF(range, criteria)Parameters
| Name | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| range | Yes | Range of cells that you want to count |
| criteria | Yes | Condition to determine whether the cell if counted or not |
Examples
Example using numbers
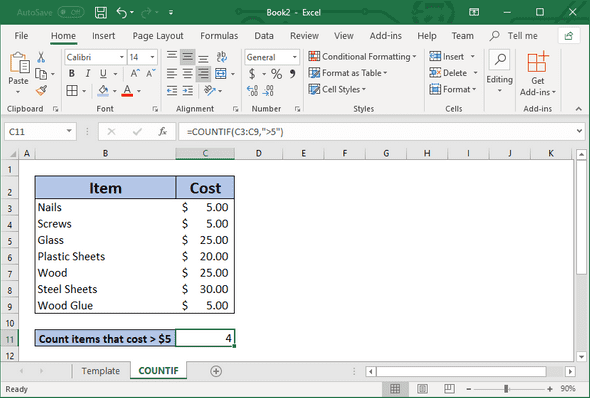
To count the number of items that cost over $5 can be easily calculated by using the COUNTIF function.
Formula
=COUNTIF(C3:C9, ">5")For more information about this example, check out this article:
Use COUNTIF to count items above $5
Example using dates
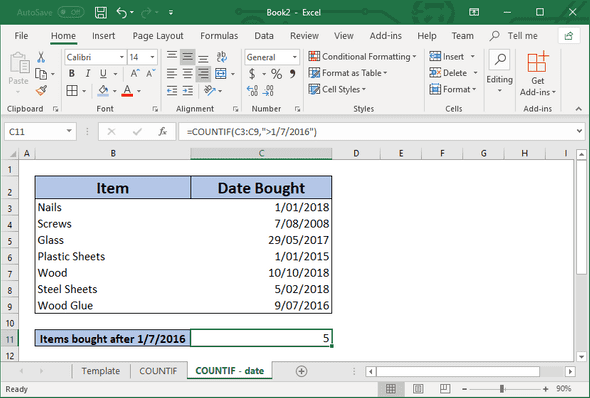
You can also use the COUNTIF function with dates. The below demonstrates how COUNTIF function can be used to only count the items that have a date greater than (after) Jan 1st, 2016.
Formula
=COUNTIF(C3:C9,">1/7/2016")For more information about this example, check out this article:
Use COUNTIF to count items past a certain date
Example using cell references
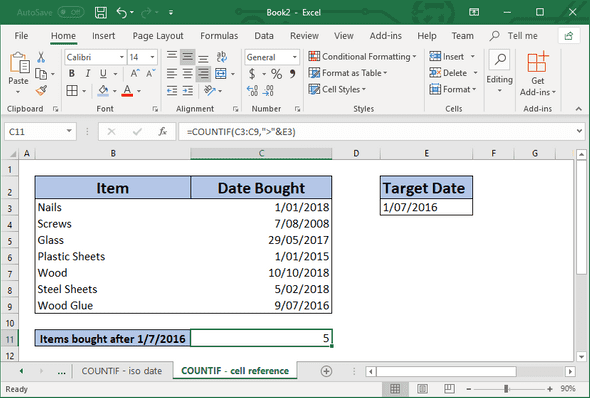
Sometimes you don’t want to compare a static (non-changing) value, but instead you want to use the value in a cell. Below is one simple example
Formula
=COUNTIF(C3:C9,">"&E3)Note
Please take note of the ”&” in front of the cell reference “E3”
For more information about this example, check out this article:
Use COUNTIF to count items past a certain date